Take The Quiz On This Post
Read the post, then take the quiz—test your knowledge and see what you’ve learned!
Introduction:
Painting is more than just a final touch in residential construction; it’s a step that impacts the longevity, aesthetics, and overall quality of your home. While choosing the right paint colour and its application correctly are important aspects, ensuring the painting process adheres to quality assurance (QA) standards is equally important.
So, how do we eliminate painting as a common defect?
I wish it were as simple as saying, "just do better painting." Unfortunately, the quality of painting is often tied to the quality of plasterboard beneath it. For a flawless finish, both need to meet high standards.
That said, this post will focus exclusively on painting quality assurance—what it involves and how it can make a lasting difference.
In the near future, we’ll share more about painting quality control, including our Paint Stage Inspection Checklist and a detailed explanation.
Quality assurance in painting involves maintaining records throughout the painting process to ensure that every step—from surface preparation to final application—meets Australian Standards like AS3894.
These records aren’t just bureaucratic checkboxes; they’re required tools that safeguard your investment, improve accountability, and provide peace of mind for homeowners and builders alike.
In this post, we’ll explore the what, why, and how of painting quality assurance record-keeping for residential construction.
Whether you’re a homeowner curious about your contractor’s processes or a builder aiming to improve your practices, this guide will break down the essential elements of QA record-keeping in simple terms.
By the end of this article, you’ll know what quality assurance entails, the key records involved, and why they’re so important for maintaining the integrity and durability of your home’s paintwork.
What is Painting Quality Assurance?
Painting quality assurance (QA) is the process of ensuring that every step of the painting process—from surface preparation to application and curing—is completed according to industry standards and best practices. In house construction, this process is particularly important as it directly impacts the durability, appearance, and value of your home.
QA in painting involves record-keeping to track and document the conditions, methods, and materials used.
These records serve multiple purposes:
- They ensure compliance with Australian Standards, such as AS3894 (site testing of protective coatings).
- They provide a clear trail of accountability for contractors and supervisors.
- They serve as a reference for future maintenance or warranty claims.
What Does QA Record-Keeping Include?
Key documents used in painting QA record-keeping include:
- Coating Inspection Report (I-20A): Tracks the details of the paint system used, including the type of coating, thickness, and application method.
- Equipment Report (I-20B): Documents the condition and calibration of the tools/equipment used, ensuring that tools meet required standards.
- Ambient and Surface Conditions Report (I-20C): Records weather conditions, substrate cleanliness, and environmental factors that can affect the outcome of the paint application.
The Role of Australian Standards in QA
In Australia, QA processes are guided by standards such as the AS3894 series, which provide detailed guidelines for testing and record-keeping relating to applied coatings.
These standards help ensure that coatings are applied in a way that will perform well under specific environmental conditions, such as high humidity or coastal exposure.
Why QA in Painting Matters
Without proper QA processes, issues like peeling, cracking, or uneven finishes can arise. QA ensures that:
- Surfaces are properly prepared before painting.
- The correct type and amount of paint are applied.
- Environmental conditions during application are suitable for optimal results.
Why is Painting Quality Assurance Important?
Painting quality assurance (QA) isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s an important part of ensuring that your home’s paintwork is durable, aesthetically pleasing, and fit for purpose. Without QA processes and records, even the most expensive paints and professional application techniques can fail to deliver the results you expect.
Ensures Adherence to Standards
QA ensures that every stage of the painting process meets Australian Standards, such as AS3894 for site testing of protective coatings. These standards are designed to:
- Ensure the paint adheres properly to surfaces.
- Verify that the correct methods and materials are used.
- Confirm environmental conditions, like humidity and temperature, are within acceptable ranges.
Adhering to these standards reduces the risk of defects such as peeling, bubbling, or cracking, which can result from improper application or poor environmental conditions.
Supports Long-Term Durability and Performance
A well-executed QA process ensures that the paintwork can withstand environmental conditions and everyday wear and tear. This is particularly important in Australia, where homes are exposed to harsh sunlight, high humidity, and coastal salt spray in some regions. QA ensures that:
- Coating systems are suitable for the environment.
- Paint is applied with consistent thickness for durability and livability.
- Surfaces are prepared to allow for optimal adhesion.
Facilitates Warranty Claims and Maintenance
In many cases, paint manufacturers offer warranties for their products, but these warranties are contingent on proper application and record-keeping. QA records provide essential documentation to support warranty claims, as they show:
- The exact paint and equipment used.
- That Australian Standards were followed.
- That conditions during application were suitable.
These records also serve as a valuable reference for future maintenance, helping contractors understand the original paintwork and replicate it if needed.
Prevents Costly Mistakes
Without proper QA, small errors during the painting process can lead to significant problems, such as:
- Paint that peels or bubbles due to insufficient surface preparation.
- Uneven finishes caused by improper application techniques.
- Premature fading due to the use of unsuitable products for specific environments.
Documenting and monitoring the painting process allows contractors to identify and address issues early, saving time and money.
Builds Trust and Accountability
For homeowners, QA is a way to ensure that contractors are doing the job right. By reviewing QA records, homeowners can:
- Confirm that their paint job was completed professionally.
- Understand the materials and methods used.
- Hold contractors accountable if problems arise.
For builders and contractors, QA processes demonstrate professionalism and a commitment to delivering quality work. It’s a win-win situation that ensures transparency and peace of mind for all parties.
When to Use QA Record-Keeping in Painting
Painting quality assurance (QA) record-keeping is required at multiple stages of the painting process. By documenting each step, contractors can ensure compliance with standards, prevent issues, and provide a transparent process for homeowners.
Below are the key stages where QA record-keeping is most valuable.
1. Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is the foundation of a quality paint job. QA records during this stage include:
- Surface Cleanliness: Verifying the surface is free from dust, grease, or rust using methods such as abrasive blasting.
- Condition of Substrate: Recording substrate condition (e.g., level of rust, profile after blasting).
- Preparation Method: Documenting whether preparation met standards like AS1627.4 for abrasive blasting.
- Surface Testing: Ensuring surfaces meet required roughness or smoothness levels for proper paint adhesion.
Why It’s Important:
Surfaces that are inadequately prepared can lead to poor adhesion, causing paint to peel or fail prematurely.
2. Coating Application
QA documentation is critical during the actual application of paint. This includes:
- Coating System Details: Recording the type of paint, batch numbers, and the number of coats applied.
- Application Methods: Noting the use of brushes, rollers, or spray equipment and verifying their suitability for the project.
- Film Thickness: Measuring wet and dry film thickness (AS3894.3) to ensure the coating meets specifications.
Why It’s Important:
Recording these details ensures consistent application and prevents issues like uneven coverage or incorrect thickness.
3. Ambient and Surface Conditions
Weather and environmental conditions can significantly impact the quality of a paint job. QA records should include:
- Weather Monitoring: Recording temperature, humidity, and dew point throughout the day (AS3894.7).
- Substrate Temperature: Ensuring the surface is within the acceptable temperature range for painting.
- Dew Point Analysis: Verifying that the surface temperature is above the dew point to prevent moisture issues.
Why It’s Important:
Poor environmental conditions can cause paint to cure incorrectly, leading to weak adhesion or uneven finishes.
4. Post-Application Inspection
After the paint has been applied, QA records are used to verify that the work meets specifications:
- Curing and Drying Times: Confirming that coatings have been given adequate time to dry and cure as per manufacturer recommendations.
- Adhesion Testing: Conducting tests (e.g., AS3894.9) to ensure the paint adheres properly to the surface.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for uniformity, colour consistency, and surface defects.
Why It’s Important:
This stage identifies any potential issues before the project is completed, allowing for immediate corrections if needed.
5. Periodic Inspections During Multi-Stage Projects
For large or ongoing residential construction projects, QA record-keeping should be performed periodically:
- Multi-Coat Systems: Verifying that each layer of coating has cured properly before applying the next.
- Equipment Rechecks: Ensuring that equipment remains calibrated and in good working order throughout the project.
- Site Adjustments: Documenting changes in environmental conditions that might require modifications to the painting process.
Why It’s Important:
Ongoing QA ensures that quality is maintained throughout the project, avoiding cumulative errors.
6. Handover and Final Documentation
At the end of the painting process, QA records are finalised and handed over to the homeowner or builder. This includes:
- A summary of all completed reports (Coating Inspection, Equipment Report, Ambient Conditions).
- A clear pass/fail status for each stage of the process.
Any recommendations for future maintenance or touch-ups.
Why It’s Important:
Comprehensive records provide peace of mind for homeowners and serve as a valuable reference for future work.

Key Components of QA Record-Keeping
Painting quality assurance (QA) record-keeping involves detailed documentation across various stages of the painting process. These records ensure compliance with Australian Standards, promote accountability, and support long-term maintenance. Below, we break down the essential components of QA record-keeping.
This is based on the Wattyl Quality Assurance Record Keeping Document I-20A:
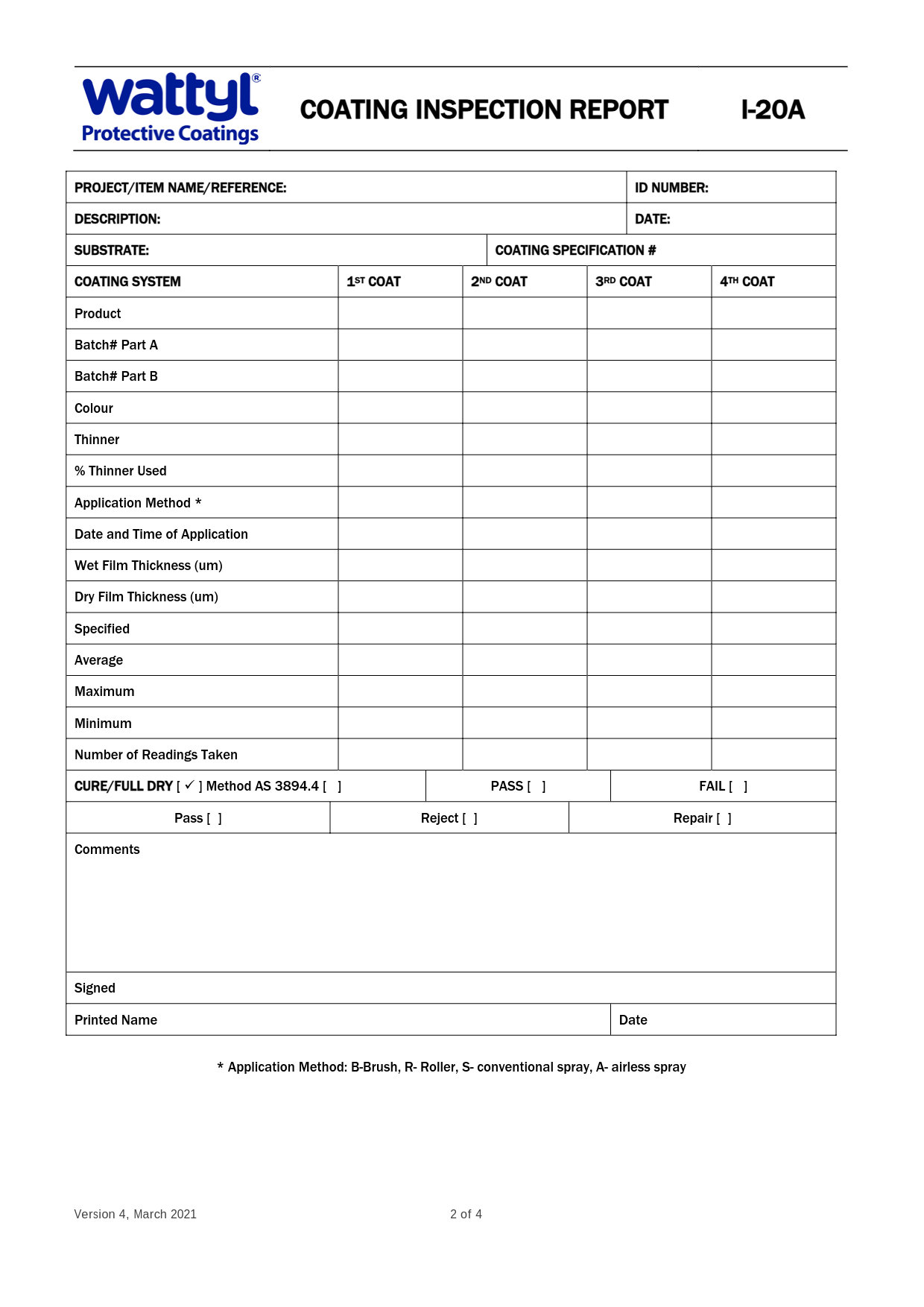
1. Coating Inspection Report (I-20A)
The Coating Inspection Report is the backbone of painting QA, the painter captures all details about the coating system used. The key elements include:
- Coating System Details: Type of paint, batch numbers, colour, and manufacturer specifications.
- Number of Coats: Details about each coat applied (e.g., primer, intermediate, and finish).
- Application Method: Tools used, such as brushes, rollers, or airless spray systems.
- Film Thickness:
- Wet Film Thickness (WFT): Measured during application to ensure proper coverage.
- Dry Film Thickness (DFT): Measured after curing to verify compliance with specifications.
Why It Matters:
Ensures the paint system is applied correctly, prevents issues like under-coating or over-coating, and supports warranty claims.
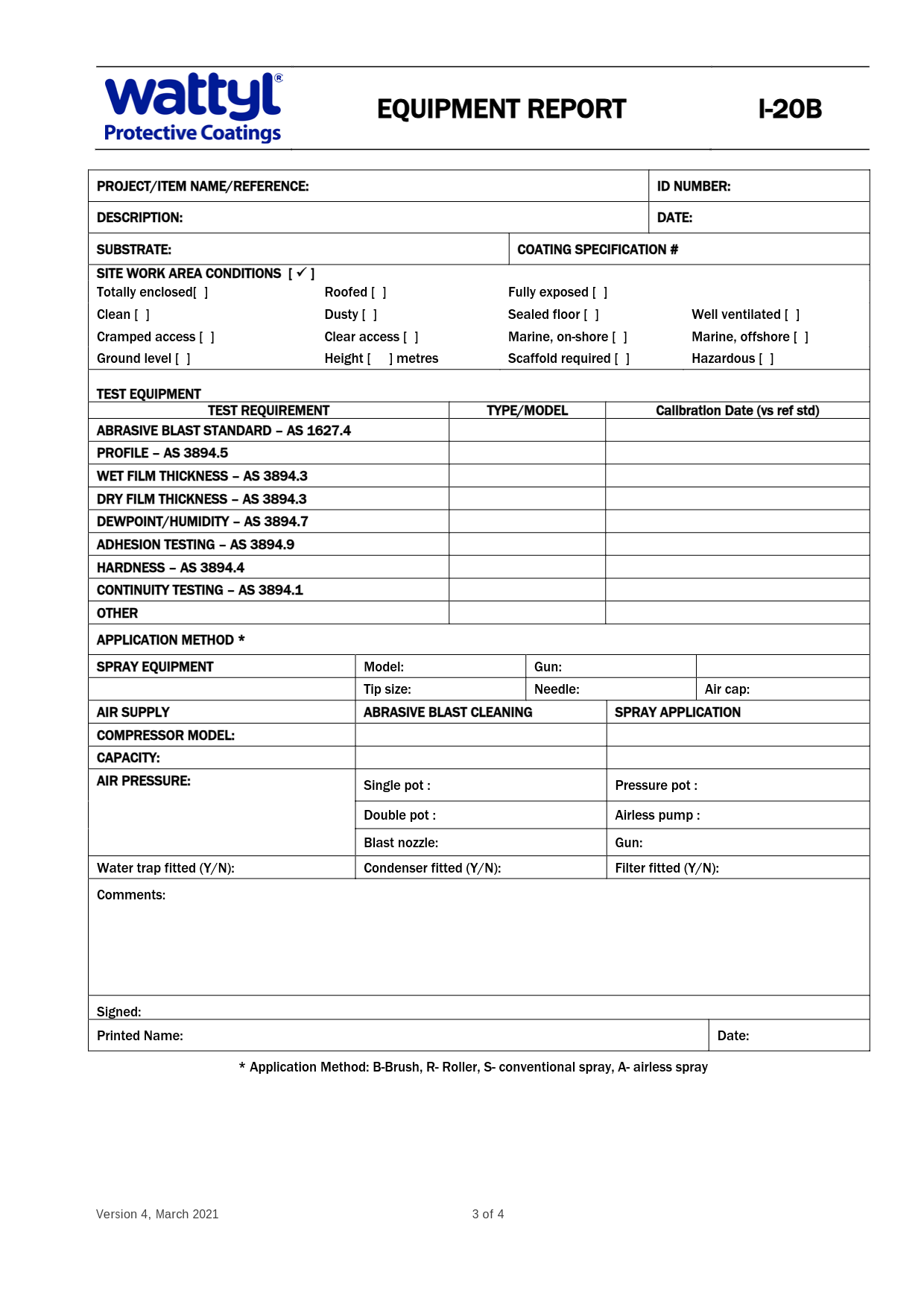
2. Equipment Report (I-20B)
The Equipment Report focuses on the tools and machinery used during the painting process. Key details include:
- Condition of Equipment:
- Calibration of spray guns, air compressors, and abrasive blasting tools.
- Verification of proper maintenance (e.g., clean filters, functioning water traps).
- Application Parameters:
- Nozzle size, air pressure, and tip settings for spray equipment.
- Suitability of equipment for the type of paint and surface conditions.
Why It Matters:
Well-maintained and calibrated equipment ensures consistent application and prevents defects caused by faulty tools.
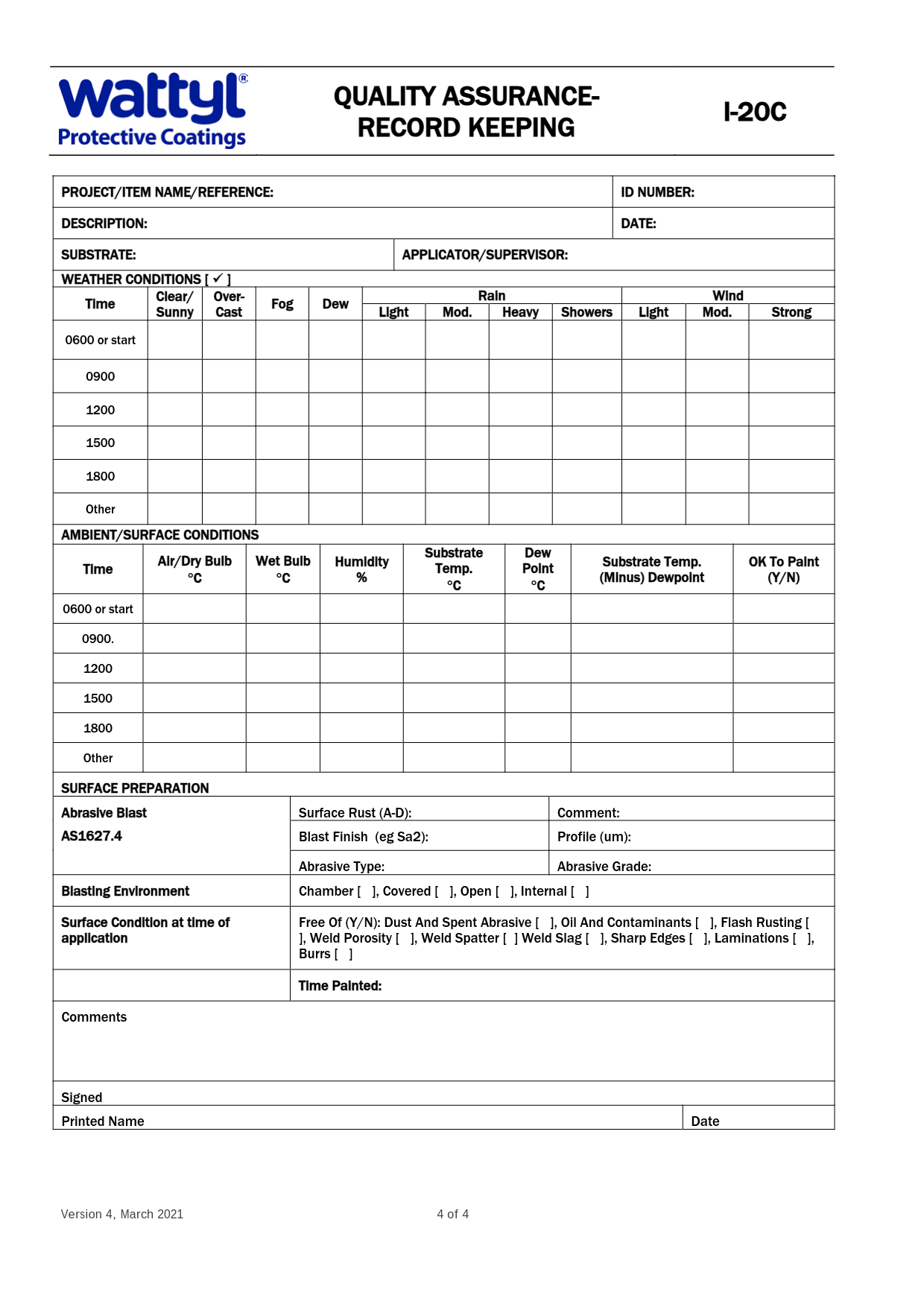
3. Ambient and Surface Conditions Report (I-20C)
This report documents environmental factors that can significantly affect paint performance. Key elements include:
- Weather Conditions:
- Air temperature, humidity, and wind speed recorded at regular intervals (e.g., 6 AM, 12 PM, 6 PM).
- Dew Point and Substrate Temperature:
- Ensures the substrate is above the dew point to avoid condensation issues.
- Confirms conditions are suitable for paint adhesion and curing.
- Surface Cleanliness:
- Verification of surface preparation, including abrasive blasting or cleaning to remove contaminants.
Why It Matters:
Helps maintain optimal conditions for painting, ensuring durability and preventing issues like peeling or bubbling.
4. Curing and Adhesion Testing
QA documentation also includes post-application tests to ensure the paint system has been properly applied and cured:
- Cure Tests: Verifies that the coating has reached the required level of hardness.
- Adhesion Tests: Measures the bond strength between the paint and substrate.
- Continuity Tests: Identifies defects such as pinholes or voids in the coating.
Why It Matters:
Confirms the integrity of the paint system and prevents costly rework.
5. Checklist for QA Record-Keeping
For clarity, contractors can use a standardised checklist to ensure all necessary records are completed. This may include:
- Coating system specifications.
- Equipment calibration certificates.
- Ambient and substrate condition logs.
- Results of curing and adhesion tests.
- Sign-off by supervisors and inspectors.
Why It Matters:
A checklist ensures consistency and reduces the risk of incomplete records, which could impact the project’s quality.
6. Use of Digital QA Tools
Many contractors now use digital tools to streamline QA record-keeping. These tools allow:
- Real-time data entry and photo uploads.
- Automated calculations for metrics like wet film thickness.
- Cloud storage for easy access and retrieval of records.
Why It Matters:
Digital tools improve accuracy, save time, and ensure records are easily accessible for audits or disputes.

Who Fills Out QA Records and Why?
Maintaining accurate QA records for painting requires involvement from multiple stakeholders, each with specific roles and responsibilities. These records are essential for ensuring that the painting process adheres to Australian Standards and meets project specifications. Let’s explore who is responsible for QA record-keeping and why it’s important.
1. Painting Contractors
Painting contractors are typically the primary record-keepers for QA during the painting process. Their responsibilities include:
- Recording Key Details: Documenting the type of paint, application methods, environmental conditions, and coating thickness.
- Ensuring Compliance: Following Australian Standards, such as AS3894, for surface preparation, application, and testing.
- Calibrating Equipment: Ensuring that all tools and equipment are in proper working condition and recording calibration details.
Why It Matters:
Contractors are on-site during the entire painting process, making them best suited to collect accurate and real-time data.
2. Supervisors and Site Managers
Supervisors and site managers oversee the QA process to ensure that all records are accurate and complete. Their responsibilities include:
- Reviewing QA Records: Checking for consistency and adherence to standards.
- Approving Final Reports: Signing off on completed QA records before handover to the client.
- Conducting Quality Control & Assurance Checks: Verifying that contractors are following approved methods and using appropriate materials.
Why It Matters:
Supervisors act as a second layer of accountability, ensuring that contractors follow the agreed-upon specifications.
3. Independent Inspectors
In some cases, independent inspectors may be hired to audit the QA process. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting Inspections: Performing independent tests, such as adhesion or thickness checks, to verify compliance.
- Providing Unbiased Reports: Offering an objective assessment of the painting process and its outcomes.
- Certifying Work: Issuing certifications or reports that validate the quality of the paint job.
Why It Matters:
Independent inspectors add credibility to the QA process, especially for high-value projects or warranty purposes.
4. Homeowners
While homeowners are not directly involved in filling out QA records, they play an important role in ensuring the process is followed. Their responsibilities include:
- Requesting QA Documentation: Asking contractors or builders for QA records as part of the project handover.
- Reviewing Records: Checking key details, such as the type of paint used, environmental conditions, and equipment calibration.
- Understanding the Process: Gaining a basic understanding of QA to identify red flags or potential issues.
Why It Matters:
Homeowners can use QA records to verify that the paintwork was completed to a high standard and address any concerns with contractors.
5. Why QA Record-Keeping is Essential
Accurate QA record-keeping serves multiple purposes, including:
- Accountability: Ensures that contractors, supervisors, and inspectors are held accountable for their work.
- Transparency: Provides homeowners with clear evidence of compliance and quality.
- Future Reference: Offers a detailed history of the painting process, useful for maintenance or warranty claims.
- Dispute Resolution: Acts as a reliable reference in case of disagreements between homeowners and contractors.

Tips for Homeowners on QA in Painting
For homeowners, understanding painting quality assurance (QA) processes may seem overwhelming, but being informed can help ensure your new home’s paintwork meets the highest standards. Here are practical tips to help you navigate QA in painting, from hiring the right contractors to reviewing documentation.
1. Ask Your Contractor About Their QA Process
Before hiring a contractor, ask questions about their approach to QA, such as:
- Do they follow Australian Standards like AS3894?
- Do they maintain QA records such as Coating Inspection Reports, Equipment Reports, and Ambient Condition Logs?
- Are their staff trained in QA procedures and the use of relevant equipment?
Why This Matters:
A contractor with a clear and transparent QA process is more likely to deliver a high-quality result.
2. Review QA Records
Request copies of all QA records once the painting is complete. Key things to check include:
- Coating Inspection Report: Verify the paint type, application method, and film thickness measurements.
- Equipment Report: Ensure equipment was in good condition and calibrated.
- Ambient and Surface Conditions Report: Confirm that weather and substrate conditions were suitable during painting.
Why This Matters:
Reviewing these records helps ensure the painting process was completed correctly and according to standards.
3. Ensure Surface Preparation Was Done Properly
Poor surface preparation is one of the most common causes of paint failures. Look for records that confirm:
- The surface was cleaned and free of dust, oil, or rust.
- Abrasive blasting or other preparation methods met required standards.
- Substrate conditions were recorded and verified before painting.
Why This Matters:
Proper surface preparation is critical for long-lasting paintwork.
4. Be Aware of Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on paint performance. Ask your contractor:
- Did they monitor and record weather conditions such as temperature and humidity?
- Was the substrate temperature above the dew point to avoid condensation?
- Were painting conditions within the manufacturer’s recommendations?
Why This Matters:
Unsuitable environmental conditions can cause paint to peel, bubble, or fail to cure properly.
5. Request Warranty Information
A reputable contractor should provide a warranty for their work and ensure that the paint manufacturer’s warranty requirements are met. Key details to confirm include:
- The duration of the warranty.
- Any conditions or exclusions.
- Proof that QA processes were followed to validate the warranty.
Why This Matters:
A warranty provides peace of mind and a pathway to address any future issues.
6. Communicate Openly with Your Contractor
Establishing clear communication with your contractor from the start can help avoid misunderstandings. Discuss:
- Your expectations for quality and record-keeping.
- The timeline for completing and handing over QA records.
- Any concerns you may have during the process.
Why This Matters:
Good communication helps ensure a smooth project and a positive outcome.
7. Keep QA Records for Future Reference
Once you receive the QA records, store them safely for future use. These documents can be invaluable for:
- Verifying warranty claims.
- Guiding future maintenance or repainting.
- Addressing potential disputes with contractors.
Why This Matters:
QA records serve as a long-term resource to protect your investment.
Conclusion
Painting quality assurance (QA) record-keeping is an essential process that ensures the durability, appearance, and long-term performance of your home’s paintwork. By documenting every step, from surface preparation to final application, QA records provide transparency, build trust, and safeguard your investment.
For homeowners, understanding the QA process is empowering. It enables you to ask the right questions, review essential documents, and verify that your contractor follows best practices. Proper QA documentation not only ensures compliance with Australian Standards but also supports warranty claims and future maintenance needs.
Prioritising QA in painting is a step toward achieving peace of mind. By holding contractors accountable and staying informed, you can ensure your home’s paintwork stands the test of time.
Further Reading

FAQS
1. What is painting quality assurance (QA)?
Painting QA is the process of ensuring that all stages of painting—from surface preparation to application and curing—are completed according to industry standards. It involves detailed record-keeping to document conditions, methods, and materials used.
2. Why is QA record-keeping important in painting?
QA records ensure compliance with Australian Standards, verify the quality of work, support warranty claims, and help prevent issues like peeling, cracking, or fading over time.
3. What are the key QA documents for painting?
The main QA documents include:
- Coating Inspection Report (I-20A): Tracks paint type, thickness, and application method.
- Equipment Report (I-20B): Documents equipment condition and calibration.
- Ambient and Surface Conditions Report (I-20C): Records environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.
4. Who is responsible for filling out QA records?
Coating contractors, supervisors, and sometimes independent inspectors are responsible for creating and maintaining QA records. Homeowners should review these records during project handover.
5. How can I ensure my contractor follows QA processes?
Ask your contractor about their QA practices, request to see previous QA records, and ensure they comply with Australian Standards like AS3894.
6. Can QA records help with warranty claims?
Yes, QA records provide detailed documentation that proves the paintwork was done according to manufacturer and industry standards, which is often required for warranty claims.
7. Why are environmental conditions important in painting?
Factors like humidity, temperature, and dew point can affect paint adhesion and curing. Recording these conditions ensures the paint is applied under optimal circumstances.
8. What happens if QA records are incomplete?
Incomplete records can lead to disputes, difficulty in claiming warranties, and uncertainty about the quality of the work performed.
9. Do I need an independent inspector for QA?
While not always required, hiring an independent inspector can add credibility to the QA process and provide an unbiased review of the painting quality.
10. How should I store QA records?
Keep QA records in a safe and easily accessible location. They are invaluable for future maintenance, repainting, or resolving disputes.
11. Is Quality Assurance different from Quality Management?
Yes, they are different but closely related. Quality Management encompasses the entire process of ensuring quality throughout a construction project, including planning, assurance, and control. Quality Assurance, as detailed in this post, focuses specifically on documenting the conditions, materials, and processes to ensure that the work meets predefined standards. In contrast, Quality Control involves inspecting and testing the work to identify and correct any deviations.
In the near future, we will publish a painting quality control checklist as part of a comprehensive construction quality management system. This checklist will provide detailed guidance on paint preparation, application, and inspection.
Want to learn more about Paint & Plasterboard?
Sign up as a free member to Constructor then visit our members Resources section on Paint & Plasterboard








